Why Does Bamboo Mold? Top Tips to Prevent It Effectively
Why does bamboo mold? And How to Prevent?
Bamboo is renowned for its strength and eco-friendly attributes. However, it can sometimes encounter an unexpected issue: Mold. To manage and prevent mold effectively, it’s crucial to understand the factors that contribute to mold growth on bamboo. This article explores why bamboo becomes moldy and how to prevent and address this problem.
Answer of Question:Does Bamboo Mold?
Yes, bamboo can mold if it is exposed to excessive moisture or humidity for extended periods. Being a natural material, bamboo is highly sensitive to its environment. When stored or used in damp conditions, such as in bathrooms or kitchens with poor ventilation, bamboo absorbs moisture, which can lead to mold growth. However, the good news is that with proper care and maintenance, you can prevent bamboo products from molding.
Why Does Bamboo Get Moldy?
Composition of Bamboo
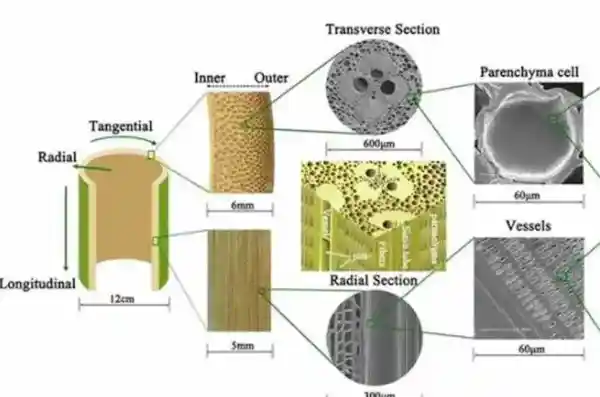
Bamboo, while resilient, has characteristics that make it vulnerable to mold. Its fibrous structure, combined with high moisture content, creates a favorable environment for mold spores.
Bamboo’s natural organic materials, including sugars and proteins, can retain moisture, which further supports mold growth. This inherent property makes bamboo a potential breeding ground for various types of mold if not properly maintained.
Environmental Factors
Mold growth on bamboo is closely linked to environmental conditions:
- Moisture: Bamboo exposed to high humidity or wet conditions absorbs moisture through its fibers. This excess moisture facilitates mold growth, as mold thrives in damp environments. Waterlogged bamboo provides an ideal breeding ground for mold spores.
- Poor Ventilation: Inadequate air circulation around bamboo allows moisture to linger, creating an environment where mold can flourish. Proper ventilation is essential to ensure that moisture evaporates efficiently and does not accumulate.
- Temperature: Warm and humid conditions accelerate mold growth. In tropical and subtropical climates, where bamboo is often used, the combination of heat and humidity can exacerbate mold issues.
Types of Mold
Several mold species can affect bamboo, each with its characteristics:
- Aspergillus::This mold prefers humid environments and can break down bamboo’s organic materials, leading to structural damage. Aspergillus can also produce allergens that may pose health risks.
- Penicillium:Common in damp conditions, Penicillium can discolor bamboo and emit musty odors. It also contributes to the deterioration of bamboo’s quality over time.
- Cladosporium:This mold is known for its dark green or black spots on bamboo surfaces. It thrives in environments with high humidity and poor air circulation.
These molds can cause significant issues, including changes in bamboo’s color, unpleasant smells, and a decrease in its durability and structural integrity.
Preventing and Managing Mold
Proper Storage
To prevent mold growth, store bamboo products in dry, well-ventilated areas. Ensure that bamboo is kept away from direct sources of moisture, such as leaks or damp walls. Using dehumidifiers in storage areas can help maintain appropriate humidity levels and prevent mold from taking hold.
Surface Treatments
Applying mold-resistant coatings or sealants to surfaces can help create a barrier against mold. These treatments can also enhance bamboo’s resistance to moisture and environmental damage, providing added protection.
Regular Inspections
Frequent inspections of bamboo items, especially those exposed to high humidity or moisture, are essential. Look for signs of mold, such as discoloration or a musty odor. Early detection allows for prompt action, preventing further damage and ensuring the bamboo remains in good condition.
Humidity Control
Maintaining optimal humidity levels is crucial for preventing mold. Utilize dehumidifiers, air conditioners, or ventilation fans to control the moisture in the air. Reducing ambient humidity helps keep it dry and less susceptible to mold growth.
Sunlight Exposure
Regular exposure to sunlight is beneficial for bamboo. UV light from the sun has natural mold-killing properties and helps evaporate moisture from bamboo surfaces. Periodically placing bamboo items in the sun can help reduce mold risk and keep them dry.
Deep Carbonization

Deep carbonization is a process that involves heating bamboo to high temperatures in a controlled environment. This treatment reduces moisture content and destroys sugars that mold feeds on, making bamboo more resistant to mold growth. Carbonized bamboo also has enhanced durability and a unique appearance.
Conclusion
Understanding why bamboo becomes moldy involves examining its composition and the environmental factors that support mold growth. By implementing effective storage practices, surface treatments, regular inspections, humidity control, and sunlight exposure, you can prevent and manage mold issues. Embracing these strategies will help maintain bamboo’s durability and usability over time.
Bamboo remains a valuable and sustainable material when properly cared for. By addressing mold concerns and adopting preventative measures, we can extend the life of bamboo products and continue to enjoy their benefits in various applications.

